Read more
AP Roaming for Enterprise Wireless Networks Without CAPWAP Tunnels
To enhance user experience and achieve seamless WiFi roaming, there are 2 common solutions:
- Planning the area to be roamed in a layer 2 network as far as possible, but the larger the layer 2 network, the less secure it is;
- Establishing tunnels between the old and new gateways and transmitting roamed endpoint traffic to the original gateway for forwarding through a centralized gateway controller, which in turn leads to complex configurations and inefficient traffic forwarding paths that affect roaming performance.
What is CAPWAP Tunnel in Enterprise Wireless Networks?
A CAPWAP tunnel is a logical connection between a wireless access point (AP) and a wireless LAN controller (WLC). It is used to transport traffic between the AP and the WLC, including data from wireless clients, control traffic from the WLC to the AP, and manage traffic from the WLC to the AP.
CAPWAP tunnels are typically created using the CAPWAP protocol, which is a proprietary protocol developed by Cisco. The CAPWAP protocol provides a number of features that make it well-suited for use in wireless networks, including:
- Centralized management: The WLC can centrally manage all of the APs in the network, including configuration, firmware updates, and security settings.
- Data encryption: All traffic between the AP and the WLC is encrypted, providing a secure environment for data transmission.
- Fault tolerance: If a CAPWAP tunnel fails, the WLC can automatically re-establish the tunnel with the AP.
CAPWAP tunnels are an essential part of any wireless network that uses WLC. They provide a secure and reliable way to transport traffic between the APs and the WLC, and they enable the WLC to centrally manage all of the APs in the network.
Benefits & Shortcomings of CAPWAP
Here are some of the benefits of using CAPWAP tunnels:
- Centralized management: CAPWAP tunnels allow a single WLC to manage multiple APs. This can save time and resources, as it eliminates the need to configure each AP individually.
- Improved security: CAPWAP tunnels encrypt all traffic between the WLC and the APs. This helps to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Increased reliability: CAPWAP tunnels are more reliable than other methods of communication between WLCs and APs. This is because they are not affected by network congestion or interference.
However, there are a few shortcomings to CAPWAP that should be considered before deploying it on a wireless network.
Proprietary protocol. This means that it is only supported by certain APs and WLCs. For example, if you are not using Cisco APs and WLCs, you will need to find a different protocol to manage your APs.
Complex to deploy and manage. This is because CAPWAP uses a number of different protocols, such as IPsec, RADIUS, and DHCP. If you are not familiar with these protocols, you may have difficulty deploying and managing a CAPWAP network.
Finally, CAPWAP can be a single point of failure in a wireless network. If the WLC fails, all of the APs in the network will be unavailable. This is because CAPWAP tunnels are used to transport all traffic between the APs and the WLC. If the WLC fails, the CAPWAP tunnels will be broken and the APs will not be able to communicate with the WLC.
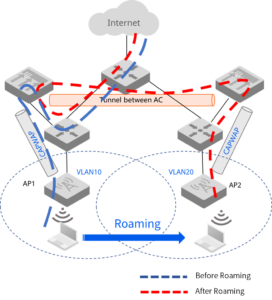
Overall, CAPWAP is a powerful protocol that can provide a number of benefits for wireless networks. However, it is important to be aware of the shortcomings of CAPWAP before deploying it in a production environment.
Another Solution for AP Roaming: Replacing centralized Wireless LAN Controller with Distributed Gateways
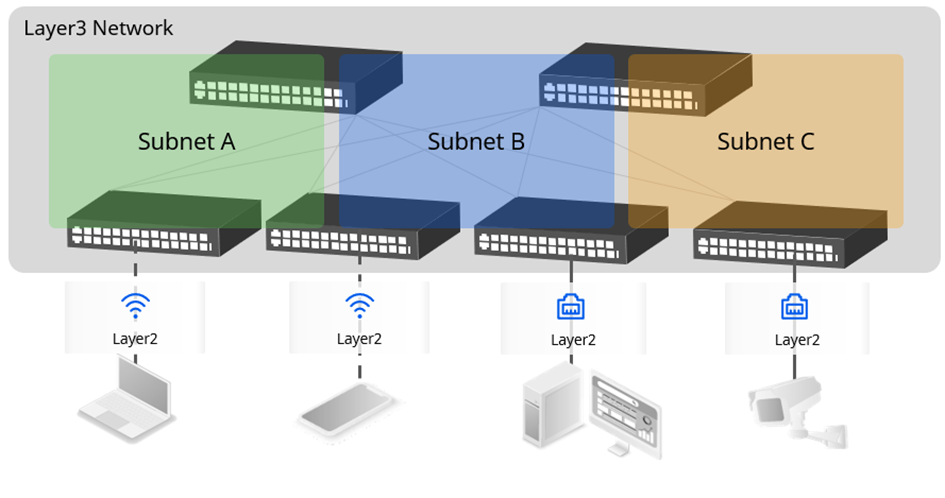
Asterfusion’s enterprise network solution is an L3 IP fabric with a unified distributed gateway running on the access layer switch, and the access layer distributed gateway synchronizes its IP/MAC information and security control policies across the network once the terminal is online.
Because the gateway information has been pre-configured on the switch accessed after terminal roaming, and the IP/MAC information of the terminal has been automatically learned and synchronized, it can respond quickly once it senses terminal roaming and automatically updates the table entry changes that occur after roaming across the network.
Centralized gateway vs. distributed gateway
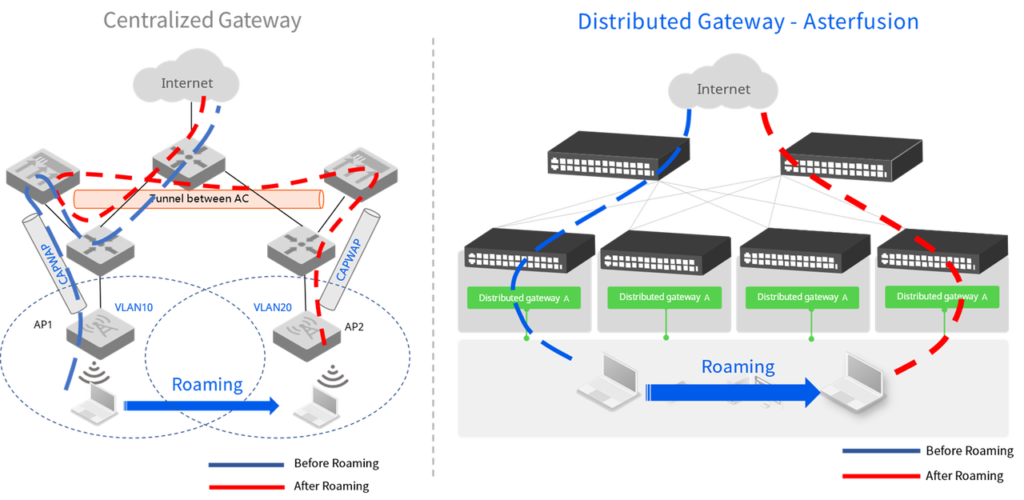
| Centralized gateway (with tunnels) | Distributed Gateway | |
|---|---|---|
| Forwarding path | Service messages are encapsulated in a tunnel and forwarded through a centralized gateway | Service messages are forwarded on the local access switch |
| O&M Deployment | Deployment requires a lot of manual configuration (e.g., AP group planning, individual SSID/VLAN, etc.) is more complex and difficult to maintain later | One-time configuration of the distributed gateway information, no additional operations are required |
| Reliability | Single point of failure, all of the APs in the network will be unavailable | Gateway functions are distributed to all access switches; failure of a single device has little impact on services |
| Scalability | High-performance, high-capacity equipment is required to carry the gateway function, limiting the rapid expansion of network size | Access layer switches only need to store local routing tables, which requires less equipment capacity and makes it easier to scale the network |
For more information, visit: https://asterfusion.com/enterprise_network/ or send email to sales@asterfusion.com
